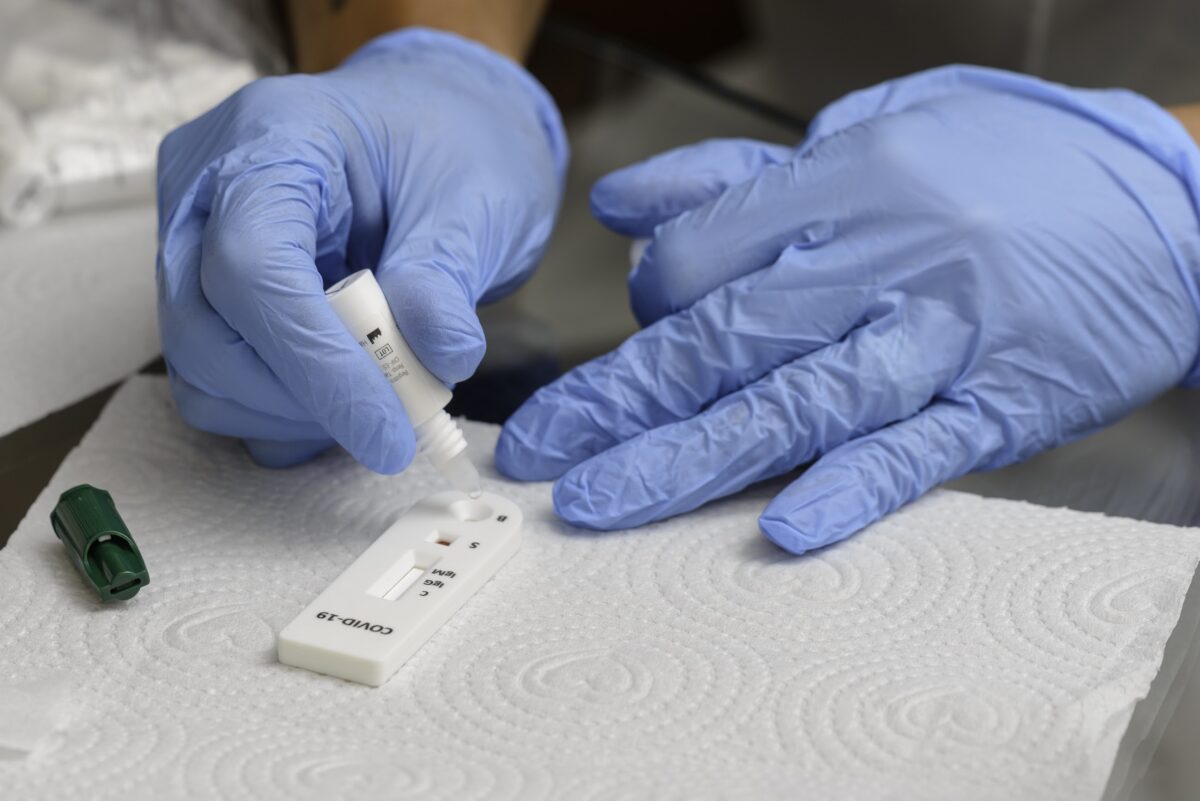
Rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) based on lateral flow assays have emerged as important diagnostic tools in the management of diseases such as malaria and COVID-19. However, errors can arise when individuals perform these tests and interpret their results. Mobile smartphone applications (apps) for reading RDTs offer a promising option to improve the accuracy of the interpretation of test results. This has been demonstrated with hardware RDT readers in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). With apps, however, no additional hardware is needed, apart from a smartphone. Such smartphones are already becoming widely available, avoiding cost, supply chain, and maintenance concerns that would occur if new hardware needed to be deployed to read RDTs.
The aim of this report is to share a summary of publicly available information about mobile applications for reading RDTs. The focus is on RDT-reading apps that do not require additional hardware beyond a mobile device (meaning a smartphone or tablet) and the RDT kit. Apps for diseases of poverty and low-resource settings are of particular interest, but the report also includes other apps, to support an understanding of this industry overall.