This guide, produced by FIND and the World Health Organization, provides information on implementing diagnostic programs using rapid antigen tests.
It shows how rapid antigen testing can be implemented to support individual case management, contact tracing, surveillance and outbreak investigations.
The guide stresses the use of strict testing protocols and clear communication, and the need to protect healthcare workers against transmission.
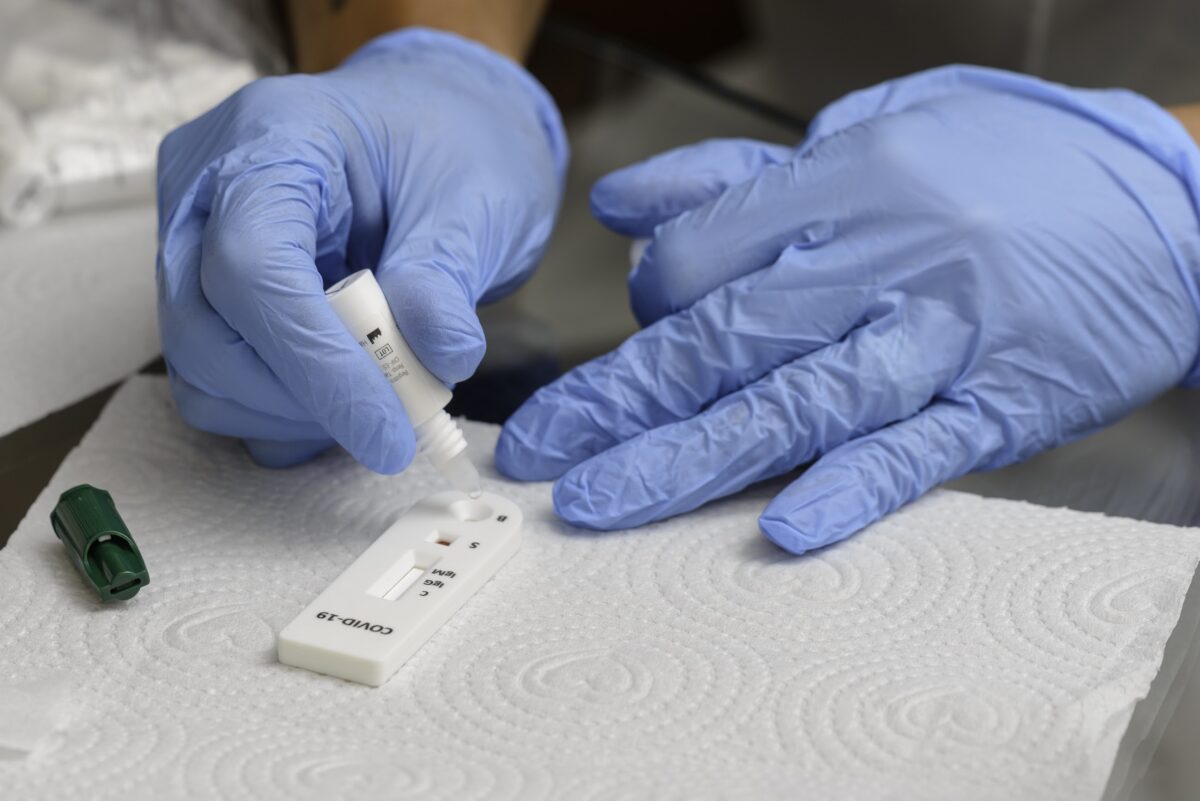
It outlines the different types of available testing and where rapid antigen testing fits in. Rapid antigen tests are used to find a protein the body produces in response to an infection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
It produces fast results and is easy to use in low-resource settings where laboratories are unavailable.
The guide provides step-by-step instructions on the use of these tests and how best to communicate and follow up on patients after a test result is obtained.
It also explains the best practice of testing within 5 to 7 days of the onset of symptoms.
While rapid tests are easy to use in most instances, the guide lists where they should not be used.
This includes testing patients without symptoms unless they are a close contact of a confirmed case; where there are no appropriate infection control measures in place; where test results will not influence the treatment of the patients and for screening at points of entry.
The use of rapid antigen tests is also not advised prior to elective surgery or blood donation.